Objects and Arrays in JavaScript part-4
What is Object in:
In the JavaScript data types tutorial, you learned about 7 different primitive data types. And here, you are going to learn about the eighth data type (JavaScript object).
JavaScript object is a non-primitive data type that allows you to store multiple collections of data.
Note: If you are familiar with other programming languages, JavaScript objects are a bit different. You do not need to create classes in order to create objects.
Here is an example of a JavaScript object.
// object
var student = {
firstName: 'ram',
class: 10
};
Here, student is an object that stores values such as strings and numbers.
JavaScript Object Declaration
The syntax to declare an object is:
var object_name = {
key1: value1,
key2: value2
}
Here, an object object_name is defined. Each member of an object is a key: value pair separated by commas and enclosed in curly braces {}.
For example,
// object creation
var person = {
name: 'John',
age: 20
};
console.log(typeof person); // object
You can also define an object in a single line.
const person = { name: 'John', age: 20 };
In the above example, name and age are keys, and John and 20 are values respectively.
JavaScript Object Properties
In JavaScript, "key: value" pairs are called properties. For example,
var person = {
name: 'John',
age: 20
};
Here, name: 'John' and age: 20 are properties.

JavaScript object properties
Accessing Object Properties
You can access the value of a property by using its key.
1. Using dot Notation
Here's the syntax of the dot notation.
objectName.key
For example,
var person = {
name: 'John',
age: 20,
};
// accessing property
console.log(person.name); // John
2. Using bracket Notation
Here is the syntax of the bracket notation.
objectName["propertyName"]
For example,
var person = {
name: 'John',
age: 20,
};
// accessing property
console.log(person["name"]); // John
JavaScript Nested Objects
An object can also contain another object. For example,
// nested object
var student = {
name: 'John',
age: 20,
marks: {
science: 70,
math: 75
}
}
// accessing property of student object
console.log(student.marks); // {science: 70, math: 75}
// accessing property of marks object
console.log(student.marks.science); // 70
In the above example, an object student contains an object value in the marks property.
JavaScript Object Methods
In JavaScript, an object can also contain a function. For example,
var person = {
name: 'Sam',
age: 30,
// using function as a value
greet: function() { console.log('hello') }
}
person.greet(); // hello
Here, a function is used as a value for the greet key. That's why we need to use person.greet() instead of person.greet to call the function inside the object.
A JavaScript method is a property containing a function declaration.
JavaScript Arrays
An array is an object that can store multiple values at once. For example,
var words = ['hello', 'world', 'welcome'];
Here, words is an array. The array is storing 3 values.
Create an Array
You can create an array using two ways:
1. Using an array literal
The easiest way to create an array is by using an array literal []. For example,
var array1 = ["eat", "sleep"];
2. Using the new keyword
You can also create an array using JavaScript's new keyword.
var array2 = new Array("eat", "sleep");
In both of the above examples, we have created an array having two elements.
Note: It is recommended to use array literal to create an array.
Here are more examples of arrays:
// empty array
var myList = [ ];
// array of numbers
var numberArray = [ 2, 4, 6, 8];
// array of strings
var stringArray = [ 'eat', 'work', 'sleep'];
// array with mixed data types
var newData = ['work', 'exercise', 1, true];
You can also store arrays, functions and other objects inside an array. For example,
var newData = [
{'task1': 'exercise'},
[1, 2 ,3],
function hello() { console.log('hello')}
];
Access Elements of an Array
You can access elements of an array using indices (0, 1, 2 …). For example,
var myArray = ['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'];
// first element
console.log(myArray[0]); // "h"
// second element
console.log(myArray[1]); // "e"

Array indexing in JavaScript
Note: Array's index starts with 0, not 1.
Add an Element to an Array
You can use the built-in method push() and unshift() to add elements to an array.
The push() method adds an element at the end of the array. For example,
var dailyActivities = ['eat', 'sleep'];
// add an element at the end
dailyActivities.push('exercise');
console.log(dailyActivities); // ['eat', 'sleep', 'exercise']
The unshift() method adds an element at the beginning of the array. For example,
var dailyActivities = ['eat', 'sleep'];
//add an element at the start
dailyActivities.unshift('work');
console.log(dailyActivities); // ['work', 'eat', 'sleep']
Change the Elements of an Array
You can also add elements or change the elements by accessing the index value.
var dailyActivities = [ 'eat', 'sleep'];
// this will add the new element 'exercise' at the 2 index
dailyActivities[2] = 'exercise';
console.log(dailyActivities); // ['eat', 'sleep', 'exercise']
Suppose, an array has two elements. If you try to add an element at index 3 (fourth element), the third element will be undefined. For example,
var dailyActivities = [ 'eat', 'sleep'];
// this will add the new element 'exercise' at the 3 index
dailyActivities[3] = 'exercise';
console.log(dailyActivities); // ["eat", "sleep", undefined, "exercise"]
Basically, if you try to add elements to high indices, the indices in between will have undefined values.
Remove an Element from an Array
You can use the pop() method to remove the last element from an array. The pop() method also returns the returned value. For example,
var dailyActivities = ['work', 'eat', 'sleep', 'exercise'];
// remove the last element
dailyActivities.pop();
console.log(dailyActivities); // ['work', 'eat', 'sleep']
// remove the last element from ['work', 'eat', 'sleep']
var removedElement = dailyActivities.pop();
//get removed element
console.log(removedElement); // 'sleep'
console.log(dailyActivities); // ['work', 'eat']
If you need to remove the first element, you can use the shift() method. The shift() method removes the first element and also returns the removed element. For example,
var dailyActivities = ['work', 'eat', 'sleep'];
// remove the first element
dailyActivities.shift();
console.log(dailyActivities); // ['eat', 'sleep']
Array length
You can find the length of an element (the number of elements in an array) using the length property. For example,
var dailyActivities = [ 'eat', 'sleep'];
// this gives the total number of elements in an array
console.log(dailyActivities.length); // 2
Array Methods
In JavaScript, there are various array methods available that make it easier to perform useful calculations.
Some of the commonly used JavaScript array methods are:
| Method | Description |
| concat() | joins two or more arrays and returns a result |
| indexOf() | searches an element of an array and returns its position |
| find() | returns the first value of an array element that passes a test |
| findIndex() | returns the first index of an array element that passes a test |
| forEach() | calls a function for each element |
| includes() | checks if an array contains a specified element |
| push() | adds a new element to the end of an array and returns the new length of an array |
| unshift() | adds a new element to the beginning of an array and returns the new length of an array |
| pop() | removes the last element of an array and returns the removed element |
| shift() | removes the first element of an array and returns the removed element |
| sort() | sorts the elements alphabetically in strings and in ascending order |
| slice() | selects the part of an array and returns the new array |
| splice() | removes or replaces existing elements and/or adds new elements |
Example: JavaScript Array Methods
var dailyActivities = ['sleep', 'work', 'exercise']
var newRoutine = ['eat'];
// sorting elements in the alphabetical order
dailyActivities.sort();
console.log(dailyActivities); // ['exercise', 'sleep', 'work']
//finding the index position of string
var position = dailyActivities.indexOf('work');
console.log(position); // 2
// slicing the array elements
var newDailyActivities = dailyActivities.slice(1);
console.log(newDailyActivities); // [ 'sleep', 'work']
// concatenating two arrays
var routine = dailyActivities.concat(newRoutine);
console.log(routine); // ["exercise", "sleep", "work", "eat"]
Note: If the element is not in an array, indexOf() gives -1.
Working on JavaScript Arrays
In JavaScript, an array is an object. And, the indices of arrays are object keys.
Since arrays are objects, the array elements are stored by reference. Hence, when an array value is copied, any change in the copied array will also reflect in the original array. For example,
var arr = ['h', 'e'];
var arr1 = arr;
arr1.push('l');
console.log(arr); // ["h", "e", "l"]
console.log(arr1); // ["h", "e", "l"]
You can also store values by passing a named key in an array. For example,
var arr = ['h', 'e'];
arr.name = 'John';
console.log(arr); // ["h", "e"]
console.log(arr.name); // "John"
console.log(arr['name']); // "John"
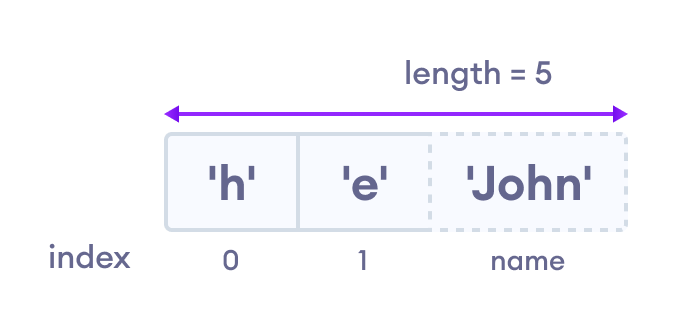
Array indexing in JavaScript
However, it is not recommended to store values by passing arbitrary names in an array.
Hence in JavaScript, you should use an array if values are in ordered collection. Otherwise it's better to use object with { }.
Thanks for reading!!